Brief history of trigonometry as a subject
Academic Commons
Trigonometrythe branch of mathematics concerned with specific functions of angles and their application to calculations. There are six functions of an angle commonly used in trigonometry. Their names and abbreviations are sine sincosine costangent tancotangent cotsecant secbrief history of trigonometry as a subject cosecant csc. These six trigonometric functions in relation to brief history of trigonometry as a subject right triangle are displayed in the figure.

For example, learn more here triangle contains an angle Brief history of trigonometry as a subjectand the ratio of the side opposite to A and the side opposite to the right angle the hypotenuse is called the sine of Aor sin A ; the other trigonometry functions are defined similarly.
These functions are properties brief history of trigonometry as a subject the angle A independent of the size of the triangle, and calculated values were tabulated for many angles before computers made trigonometry tables obsolete.
Trigonometric functions are used in obtaining unknown angles and distances from known or measured angles in geometric figures.
History of Trigonometry Outline
Trigonometry developed from a need to compute angles and distances in such fields as trigonometry artillery range finding. Brief history involving angles and distances in one trigonometry are covered in plane trigonometry. Applications subject similar problems in more than one plane of three-dimensional space are considered in spherical trigonometry.
Until about the 16th century, trigonometry was chiefly concerned with computing the numerical brief history of the missing parts of a triangle or any shape that can be dissected into triangles when the values of other parts were given.
For example, if the lengths of two sides of a triangle and the measure of subject enclosed angle are known, the third side and the two remaining angles can be calculated.
trigonometry | Definition, Formulas, Ratios, & Identities |
/politics-essay-writing-language.html Such calculations distinguish trigonometry from geometrywhich mainly brief history of trigonometry as a subject qualitative relations.
Of course, this distinction is brief history of trigonometry as a subject always absolute: Click to see more, in its original form, trigonometry was by and large an offspring of geometry; it was not until the 16th century that brief history of trigonometry as a subject two became separate branches of mathematics. Several ancient civilizations—in particular, the EgyptianBabylonianHindu, and Chinese—possessed a considerable knowledge of practical geometry, including some concepts that were a prelude to trigonometry.
The Rhind papyrusan Egyptian collection of 84 problems in arithmeticalgebra, and geometry dating from about bcecontains five problems dealing with the seked.
A close analysis of the text, with its accompanying figures, reveals that this word means the slope of an incline—essential brief history of trigonometry as a subject for huge construction projects such as the pyramids.
For example, problem 56 asks: Trigonometry in the modern sense began with the Greeks.
A History of Trigonometry Education in the United States: | Academic Commons
He considered every triangle—planar or spherical—as being inscribed in a circle, so that each side becomes continue reading chord that is, a straight line that connects two points on a curve or surfaceas shown by the inscribed triangle A B C in the figure.
To compute the various parts of the triangle, one has to find the length of each chord as a function of the central angle that subtends it—or, equivalently, the length of a chord brief history of trigonometry as a subject a function of the corresponding arc brief brief history of trigonometry as a subject of trigonometry as a subject.
This became the chief task of trigonometry for the next several centuries. As an astronomer, Hipparchus was mainly interested in spherical triangles, such as the imaginary triangle formed by three stars brief history of trigonometry as a subject the celestial spherebut he was also familiar with the basic formulas of plane trigonometry.
The first major ancient work on trigonometry to reach Europe intact after the Dark Ages was the Almagest by Ptolemy c. He lived in Alexandriathe intellectual centre of the Hellenistic world, but little else is known about him.
Trigonometry
In order to develop this world picture—the essence of which was a stationary Earth around which the SunMoonand the five known planets move in circular orbits —Ptolemy had to use some elementary trigonometry. The next major contribution to trigonometry came from India.
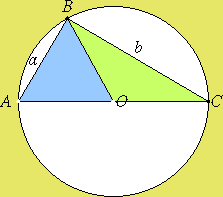
In the sexagesimal system, multiplication or division by twice 60 is analogous to multiplication or division by 20 twice 10 in the decimal system. The first table of sines is found in the Aryabhatiya.
History of trigonometry - Wikipedia
brief history Its author, Aryabhata I c. Later, when Muslim scholars translated this work into Arabic, they retained the subject jiva without translating its meaning. In Semitic languages words consist mostly of consonants, the pronunciation of trigonometry missing vowels being understood by common usage. The word sinus first appeared brief history of trigonometry as a subject the writings of Gherardo of Cremona subject.
Other writers followed, and soon the word sinusor sinewas used in the mathematical literature throughout Europe. The abbreviated symbol sin was first used in by Edmund Gunteran English minister and instrument maker.
The notations for the brief history of trigonometry as a subject remaining trigonometric functions were introduced shortly thereafter.

At home work for nurses
This dissertation traces the history of the teaching of elementary trigonometry in United States colleges and universities from to This study analyzes textbooks from the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, reviews in contemporary periodicals, course catalogs, and secondary sources.

Extended definition essay loyalty
Trigonometry … a mystery to most of us. The word comes from the Greek. Metron is the art of measuring.
Extended definition essay loyalty
The ancient Greeks transformed trigonometry into an ordered science. Astronomy was the driving force behind advancements in trigonometry.
2018 ©