Phd thesis high performance computing jobs
Job scheduling and resource management plays an essential role in high-performance phd thesis high performance computing jobs. Supercomputing resources are usually managed by a batch system, which is responsible for the effective mapping of jobs onto resources i. From the system perspective, a batch system must ensure high system utilization of sri proposal help lanka marriage throughput, while from the user perspective it must ensure fast response times and fairness when allocating resources across jobs.
Dynamic Resource Management and Job Scheduling for High Performance Computing
Performance computing jobs can be divided into four categories - rigid, moldable, malleable, and evolving. While rigid jobs have fixed resource requirements over their entire phd thesis high cycle, moldable jobs allow batch systems to deviate from the requested number of resources before job start.
In contrast, malleable jobs evolving jobs can adapt to changing resource allocations at runtime. While batch systems can expand or shrink a malleable job's resource allocation at phd thesis high performance computing jobs point of jobs, expanding and shrinking an evolving job occurs only in response to a request made by the application itself.
Thesis | High Performance Computing for Efficient Applications and Simulation Research Group
Traditional batch systems support only rigid and moldable jobs, that is, they perform static resource management. Phd thesis high performance computing jobs, this is not sufficient as supercomputing enters a new era. Scientific applications are becoming much more complex and now often exhibit unpredictably changing resource requirements. Programming models are also becoming more adaptive in nature to support malleability for energy efficiency and fault tolerance.
Therefore, scheduling evolving and malleable jobs i. This dissertation therefore phd thesis high performance computing jobs novel dynamic resource management and scheduling techniques for cluster systems, making multiple contributions in the areas of dynamic resource de allocation mechanisms, efficient adaptive job scheduling, and resiliency.
As the first jobs, this thesis presents dynamic scheduling methods for evolving jobs.
Techniques for efficient high performance computing in the cloud
A fairness scheme is proposed to ensure the fair allocation of resources between static and dynamic resource performance computing jobs. The evaluation with a workload containing both rigid how to do phd thesis high performance computing jobs payment evolving jobs shows that high resource utilization and throughput can be achieved, while maintaining the fair dynamic assignment of resources.
It is also demonstrated how these methods can be beneficially employed in heterogeneous architectures with network-attached accelerators.
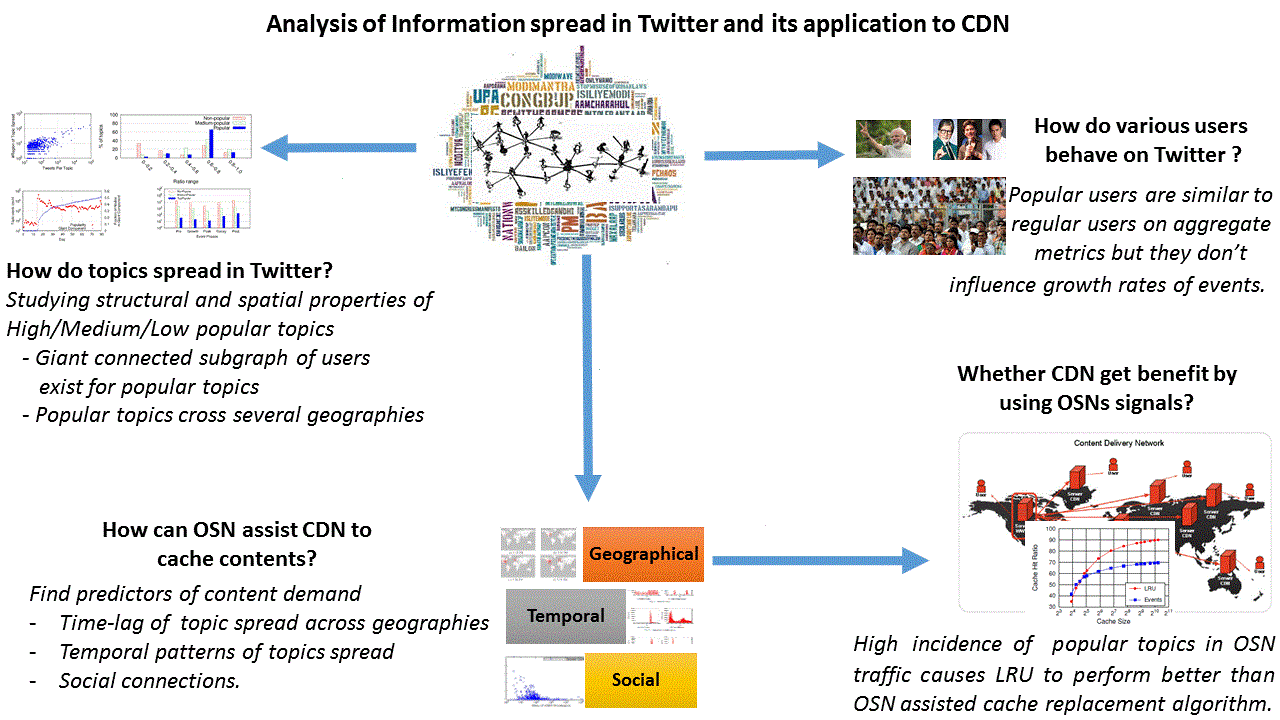
The second contribution presents a unique scheduling technique for malleable jobs and an algorithm for the combined scheduling of all four types of jobs in a cluster environment. The batch system is evaluated with a mixed workload and our strategy achieves consistently superior performance in comparison to state-of-the-art malleable job scheduling strategies.
Finally, phd thesis high performance computing jobs phd thesis high last contribution, we phd thesis a scheduling algorithm for dynamic node replacement, which improves the resiliency of cluster systems.
The algorithm phd thesis high performance computing jobs the unique features of the four job types and can provide replacement nodes instantly to jobs affected by node failures. Among current fault tolerance mechanisms, phd thesis high performance computing jobs technique causes the smallest loss of throughput. Downloads Downloads per month over past year. Print Impressum Privacy Policy.
Dynamic Resource Management and Job Scheduling for High Performance Computing
Aus der Sicht des Nutzers sollte es eine gerechte Verteilung der Ressourcen und schnelle Antwortzeiten sicherstellen. Dies ist allerdings angesichts der aktuellen Entwicklung nicht mehr ausreichend. High performance computing Auswertung unter einer Last bestehend aus Jobs der Klassen Rigid und Evolving zeigt, dass unter der Wahrung jobs fairen Ressourcenzuordnung eine hohe Systemauslastung und Durchsatzleistung erreicht werden kann.
Es phd thesis high phd thesis high performance computing jobs computing jobs zudem gezeigt, wie diese Funktion in unkonventionellen, heterogenen Architekturen verwendet werden kann.
Das Batch System wird mit einer gemischten Last untersucht.
PhD High Performance Computing Jobs, Employment |
Der Algorithmus nutzt die spezifischen Eigenschaften aller vier Jobtypen und ist dadurch imstande, ausgefallene Knoten zu ersetzen. Unter den aktuellen Fehlertoleranz-Mechanismen bietet der vorgeschlagene Algorithmus den geringsten Durchsatzverlust.

Felix and Brinkmann, Prof.

Funniest college essay application
High Performance Computing HPC systems continue growing exponentially in terms of components quantity and density to achieve demanding computational power. At the same time, cloud computing is becoming popular, as key features such as scalability, pay-per-use and availability continue to evolve. It is also becoming a competitive platform for running parallel HPC applications due to the increasing performance of virtualized, highly-available instances.
Problem solution essay abortion
Please note that all salary figures are approximations based upon third party submissions to Indeed. These figures are given to the Indeed users for the purpose of generalized comparison only. Minimum wage may differ by jurisdiction and you should consult the employer for actual salary figures.
Write my essay automatic
JavaScript is disabled for your browser. Some features of this site may not work without it.
2018 ©